Mappings: Difference between revisions
Alkitjohan (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=== Overview === | |||
[[File:Mapping v2.png|thumb|685x685px]] | |||
[[File: | The ''Mappings for this task'' window is used to configure the connections between logical communication channels (from a signal reader assignment) and the physical buses used in the system. It displays both CAN and LIN channels and allows you to assign them to specific physical buses (WCU/WMU or VCF). | ||
---- | |||
=== Left Side – Logical Channels === | |||
On the '''left side''' of each group, you can see the logical configuration: | |||
* '''Channel:''' The CAN or LIN bus identifier (e.g., CAN1, LIN1). | |||
* '''Speed:''' The communication speed of the bus (e.g., 500 kbit/s for CAN, 9600 bit/s for LIN). | |||
* '''Name:''' The assigned name of the channel. | |||
* '''#Signals:''' Number of signals currently mapped to that bus. | |||
* '''WCU:''' The drop-down menu where you assign the physical bus. | |||
This area represents the buses defined in the signal reader assignment. These are the ''logical'' buses that need to be linked to ''physical'' buses. | |||
---- | |||
=== | === Right Side – Physical Bus Selection === | ||
On the '''right side''', under the '''WCU''' column, you select the '''physical bus'''. | |||
* The physical bus can belong to a '''WCU, WMU''' or a '''VCF''' channel. | |||
* Selecting the correct WCU ensures that signals are properly routed to the physical communication hardware. | |||
* The syntax for a physical bus is: '''BUSIO:Speed:Name''' (for example: CAN1:500:CAN1). | |||
---- | |||
=== | === Automatic Mapping === | ||
The system performs '''auto-mapping''' automatically when the window is opened or refreshed. | |||
Auto-mapping works as follows: | |||
# '''Name Matching:''' The tool first tries to match logical and physical buses based on their names. | |||
# '''Bus Number Matching:''' If names don’t match, it attempts to match based on bus numbers. | |||
# '''Speed Requirement:''' The mapping only succeeds if the '''bus speeds''' are identical. | |||
If a match cannot be made, or if an error occurs, a '''red triangle''' appears next to the affected bus. | |||
---- | |||
=== Error and Warning Indicators === | |||
A '''red triangle''' will appear in the following cases: | |||
* The '''bus speed''' does not match between logical and physical buses. | |||
* The selected '''physical bus''' has already been assigned elsewhere. Each physical bus can '''only be used once''' in the mapping. | |||
A yellow triangle will appear in the following cases: | |||
* No physical bus is selected | |||
---- | |||
=== Grouping Option === | |||
In the '''top-right corner''', there is an option to choose whether '''WCUs should be grouped'''. | |||
When grouping is enabled, the system will automatically match WCUs that have: | |||
* The same number of channels, | |||
* The same I/O numbering, and | |||
* The same communication speed. | |||
When groups are created, an '''eye icon''' 👁️ and a '''number''' appear next to the group name. | |||
* Clicking the '''eye icon''' or the '''number''' displays a list of all WCUs included in that group. | |||
* The number indicates how many WCUs are currently part of the group. | |||
This grouping feature helps simplify configuration when working with multiple identical WCUs. | |||
---- | |||
=== Buttons === | |||
At the bottom of the window: | |||
* '''Save:''' Confirms and saves all mappings. | |||
* '''Restore:''' Resets everything to the ''auto-mapped'' state. (Auto-mapping is always performed first when the window opens.) | |||
* '''Close:''' Exits the window without saving changes. | |||
Latest revision as of 13:35, 12 November 2025
Overview
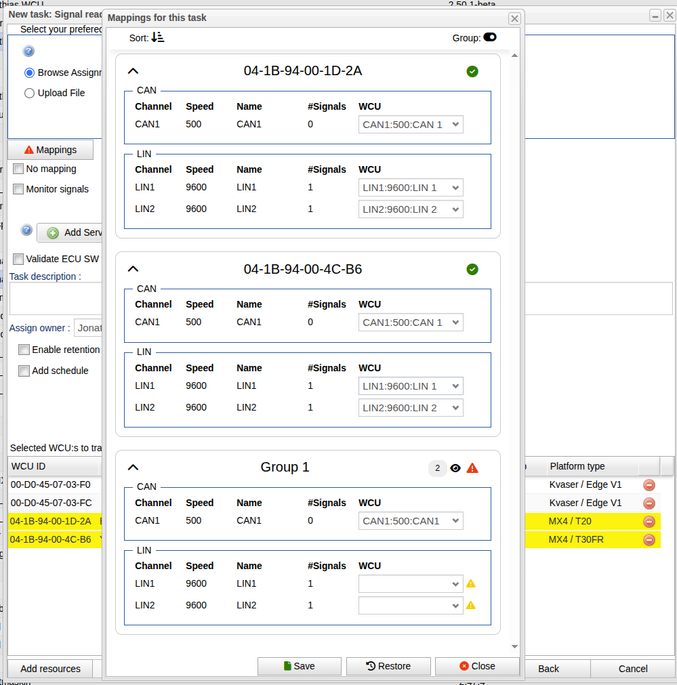
The Mappings for this task window is used to configure the connections between logical communication channels (from a signal reader assignment) and the physical buses used in the system. It displays both CAN and LIN channels and allows you to assign them to specific physical buses (WCU/WMU or VCF).
Left Side – Logical Channels
On the left side of each group, you can see the logical configuration:
- Channel: The CAN or LIN bus identifier (e.g., CAN1, LIN1).
- Speed: The communication speed of the bus (e.g., 500 kbit/s for CAN, 9600 bit/s for LIN).
- Name: The assigned name of the channel.
- #Signals: Number of signals currently mapped to that bus.
- WCU: The drop-down menu where you assign the physical bus.
This area represents the buses defined in the signal reader assignment. These are the logical buses that need to be linked to physical buses.
Right Side – Physical Bus Selection
On the right side, under the WCU column, you select the physical bus.
- The physical bus can belong to a WCU, WMU or a VCF channel.
- Selecting the correct WCU ensures that signals are properly routed to the physical communication hardware.
- The syntax for a physical bus is: BUSIO:Speed:Name (for example: CAN1:500:CAN1).
Automatic Mapping
The system performs auto-mapping automatically when the window is opened or refreshed.
Auto-mapping works as follows:
- Name Matching: The tool first tries to match logical and physical buses based on their names.
- Bus Number Matching: If names don’t match, it attempts to match based on bus numbers.
- Speed Requirement: The mapping only succeeds if the bus speeds are identical.
If a match cannot be made, or if an error occurs, a red triangle appears next to the affected bus.
Error and Warning Indicators
A red triangle will appear in the following cases:
- The bus speed does not match between logical and physical buses.
- The selected physical bus has already been assigned elsewhere. Each physical bus can only be used once in the mapping.
A yellow triangle will appear in the following cases:
- No physical bus is selected
Grouping Option
In the top-right corner, there is an option to choose whether WCUs should be grouped.
When grouping is enabled, the system will automatically match WCUs that have:
- The same number of channels,
- The same I/O numbering, and
- The same communication speed.
When groups are created, an eye icon 👁️ and a number appear next to the group name.
- Clicking the eye icon or the number displays a list of all WCUs included in that group.
- The number indicates how many WCUs are currently part of the group.
This grouping feature helps simplify configuration when working with multiple identical WCUs.
Buttons
At the bottom of the window:
- Save: Confirms and saves all mappings.
- Restore: Resets everything to the auto-mapped state. (Auto-mapping is always performed first when the window opens.)
- Close: Exits the window without saving changes.