Difference between revisions of "Preview data"
m (→Statistical data: Minor spelling correction.) |
(Added some information about Y-axis scaling) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
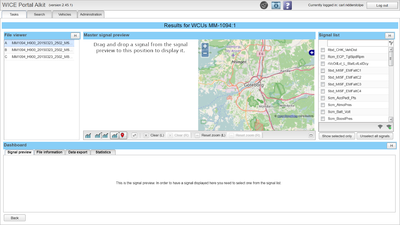
One of the main functions is to view signals as graphs and see their route. To do so you first need to select one of the files from the Source List on the left. You then select the signals you wish to preview from the list to the right. The signals which you can see are specific to the file you have selected. You can change file from the source list at any time, your previous signal selection will remain on screen. The selected signals can then be seen at the bottom of the page under the tab "Signal preview". By double clicking the thumbnail of the signal at the bottom of the page you will push it up into the master signal preview, where you have enhanced control of how you want to preview your signals. You can have up to four signals in any of the master signal preview graphs at once. You can also drag and drop the thumbnails to the master signal preview. | One of the main functions is to view signals as graphs and see their route. To do so you first need to select one of the files from the Source List on the left. You then select the signals you wish to preview from the list to the right. The signals which you can see are specific to the file you have selected. You can change file from the source list at any time, your previous signal selection will remain on screen. The selected signals can then be seen at the bottom of the page under the tab "Signal preview". By double clicking the thumbnail of the signal at the bottom of the page you will push it up into the master signal preview, where you have enhanced control of how you want to preview your signals. You can have up to four signals in any of the master signal preview graphs at once. You can also drag and drop the thumbnails to the master signal preview. | ||
== | == Y-axis scaling == | ||
By default the vertical axis is scaled based on a signals predetermined minimum and maximum values which are embedded into the MDF file. This has two advantages. Primarily it makes the same signal from two different measurements easier to compare, but it should also help display the signal using a scale that is relevant for that particular signal. There are however a set of circumstances in which this principle is abandoned in favor of auto fit: | |||
* If the signal has no default min/max values | |||
* If the signals min value is greater than its max value | |||
* If the actual signal is outside of the predetermined min/max bounds. | |||
* If the predetermined max is a lot higher than the actual max of the signal. This is to prevent the previewed signal from being displayed as nothing but a flat line at the bottom of the graph. | |||
If any of these conditions are true, then the vertical min/max will be automatically fitted to the curve based on the curves extreme values. | |||
== Features == | |||
=== Preview modes === | === Preview modes === | ||
| Line 24: | Line 32: | ||
=== '''Statistical data''' === | === '''Statistical data''' === | ||
You can see statistics for the plots and their signal(s) at the bottom under the tab "Statistics". To the left you have a | You can see statistics for the plots and their signal(s) at the bottom under the tab "Statistics". To the left you have a button for if you want to show the left or right plot. What being showed is the plots signal and x/y min/max, mean value, standard devation, total amount of data samples and shown amount of data samples for each signal. Note that the plot can only show 500 samples for each signal and therefore need to hide samples for bigger signals. The plot will always try to have an as even as possible space between the samples and if it is showing a signal with 502 signals it will show 251 as it will give the smoothest and most accurate view even if its not showing as many samples as it could. | ||
=== Export options === | === Export options === | ||
Revision as of 11:38, 17 October 2018
This is a tool used to graph signal values from MDF-files.
Example of usage
One of the main functions is to view signals as graphs and see their route. To do so you first need to select one of the files from the Source List on the left. You then select the signals you wish to preview from the list to the right. The signals which you can see are specific to the file you have selected. You can change file from the source list at any time, your previous signal selection will remain on screen. The selected signals can then be seen at the bottom of the page under the tab "Signal preview". By double clicking the thumbnail of the signal at the bottom of the page you will push it up into the master signal preview, where you have enhanced control of how you want to preview your signals. You can have up to four signals in any of the master signal preview graphs at once. You can also drag and drop the thumbnails to the master signal preview.
Y-axis scaling
By default the vertical axis is scaled based on a signals predetermined minimum and maximum values which are embedded into the MDF file. This has two advantages. Primarily it makes the same signal from two different measurements easier to compare, but it should also help display the signal using a scale that is relevant for that particular signal. There are however a set of circumstances in which this principle is abandoned in favor of auto fit:
- If the signal has no default min/max values
- If the signals min value is greater than its max value
- If the actual signal is outside of the predetermined min/max bounds.
- If the predetermined max is a lot higher than the actual max of the signal. This is to prevent the previewed signal from being displayed as nothing but a flat line at the bottom of the graph.
If any of these conditions are true, then the vertical min/max will be automatically fitted to the curve based on the curves extreme values.
Features
Preview modes
"Master signal preview" has three different preview modes which you can select from the bottom left corner of the "Master signal preview" window. The default view is "Map split", which has one graph on the left, and a map on the right where the cars route will be shown (if GPS data is available). The second mode is the split mode, which splits the window into two graphs. This could be useful for comparing different signals. Finally, there is the "single" mode which allows you to utilize as much space as you can for one single graph.
Window size
If you want to have a bigger "Master signal preview" you can press the fullscreen button on the bottom right of the Master signal preview window, or you can manually hide other areas you do not wish to see by pressing the "H" on them. To show the areas again you can press the "S".
Switching between plots
There are always two plots even though there might only be one shown. This means you can always use the button "Switch" to make the plots switch places. When there are two plots shown they switch positions but when there is only one plot shown the shown plot (the left one) will switch with the hidden plot (the right one). This can be useful when comparing signals.
Zooming
To zoom in on graphs you drag between two points(not necessarily data points) on the graf and it will zoom in between those two points.To zoom out you press "Reset zoom" for L or R depending on which plot you want to zoom out. Notice that "Zoom out (R)" is only clickable when you show two plots and that is because even if there always are two plots you can only zoom out and clear shown plots.
Map
When clicking on a point in the graph you will see where the car was for that given time value on the map. Note that this only works if such GPS data is available.
Statistical data
You can see statistics for the plots and their signal(s) at the bottom under the tab "Statistics". To the left you have a button for if you want to show the left or right plot. What being showed is the plots signal and x/y min/max, mean value, standard devation, total amount of data samples and shown amount of data samples for each signal. Note that the plot can only show 500 samples for each signal and therefore need to hide samples for bigger signals. The plot will always try to have an as even as possible space between the samples and if it is showing a signal with 502 signals it will show 251 as it will give the smoothest and most accurate view even if its not showing as many samples as it could.
Export options
At the bottom you can also download a plot as a text file. Under the tab "Data export" you select which plot you want to download, select between which time values it should download data points, set a download description (optional) and then press "To text file" to make the file ready for download. The text file you download is supported in Excel.
Saving signals
You can save the currently selected signals by pressing the signal symbol with a plus on it located on the bottom right of the "Signal List". This allows you to reload these signals in any source as long as that source contains signals with exactly matching names.
Quick selection mode
This selection mode allows you preview the same set of signals from an array of files with ease. Here is how it works:
- This requires you to have selected two or more files before you entered the signal preview interface.
- Beneath the source list to the left you will find a checkbox that says "Quick selection mode". Click it.
- Select a file by clicking on a file in the source list.
- Select any number of signals in the signal list.
- If you want to add any of the signals into the master preview, then do so by dragging and dropping (or double clicking) the thumbnails as usual.
- You can now swap between files by selecting any file you like from the source list. When you swap file the signals you selected previously will now be selected again in the new file.
Notice: This will only work if both files have signals with the exact same name. Any deviation in signal naming will cause the program to be unable to find the signal, thus skipping it and moving on to the next signal